- 6 Factors that Determine Eco-Friendliness
- Environmental Performance Data
- Siding Eco-Friendliness Comparison Table
- Other Ways to Improve Energy Performance
More and more, homeowners are looking for sustainable, eco-friendly siding options for their homes. However, choosing the most sustainable siding is not always as straightforward as you might assume. While wood siding might seem like the obvious choice, in practice it is not always the case.
The reason for this is that in addition to material type, there are 5 other factors that must be taken into account when determining eco-friendliness:
6 Factors that Determine Eco-Friendliness
For the environmentally conscious homeowner, the choice of new siding will strong depend on its sustainability. Sustainability is determined by the following criteria:
- How long does the material last?
- Does the material contribute to health problems?
- How much maintenance is required?
- End of life – Can the material be recycled? Is it biodegradable in landfills?
1) Material
Simple questions you can ask when determining how green a siding material is:
- Is the siding toxic?
- Is the siding biodegradable?
- Does it come from nature?
- Is it man-made?
- Is it certified green?
2) Labor
The more complex and heavy the siding is, the more expensive it will be to install. Rare material, too, will be more expensive. Stone, for example, will require more energy at the outset to install.
3) Energy Efficiency
The R-value of siding reflects the insulation properties. Higher R-values mean that the siding will preserve heat better, and keep the exchange of interior and exterior temperatures to a minimum.
4) Recyclability
Can the siding you consider be recycled? If not, it may be salvaged, rather than taken to a landfill. In addition, every siding job has from 10% to 15% waste. Can the new materials be recycled or salvaged?
5) Manufacturing
Does the manufacturing of your siding of choice require a lot of energy? For example, the manufacturing of brick requires a great deal of energy, since the bricks are baked for days at 2,000+ degrees.
This is much like the debate over whether or not to request paper bags or plastic bags at the grocery store. Paper bags are made from trees, while plastic bags require the use of petrochemicals for production. The good news is that cedar shingles and siding are mostly made from salvaged wood.
6) Locally Sourced
If your material can be locally sourced, you reduce your carbon footprint. Cedar shingles or aluminum siding that is manufactured nearby does not have to be trucked across the country, which increases waste.
Environmental Performance Data
The U.S. Green Building Council has established guidelines for determining whether or not a building can be certified as “green.” LEED certification gives points for sustainability, environmentally-safe, and eco-friendly construction.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides a free software tool Building for Energy and Environmental Sustainability tool (BEES 2.0) which which allows users to conduct their own environmental analyses to determine the sustainability performance measures of building products over their life cycle.
The tool takes the following steps of the life cycle into consideration: raw materials, manufacturing, transportation, installation and end of life and determines the estimated impact to metrics including global warming, smog, acidification, water use and energy demand. Surprisingly, vinyl siding does quite well when it comes to environmental impact.
Using the BEES tool, our results showed the following:
Siding Eco-Friendliness Comparison Table
| Type | Efficiency | Labor | Material | Local | Manufacturing | Recycling | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 22 |
| Metal | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 20 |
| Stucco | 4 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 20 |
| Adobe & Earth Products | 5 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 28 |
| Fiber Cement | 3 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 16 |
| Brick | 4 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 18 |
| Stone | 4 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 22 |
| Vinyl | 2 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 13 |
1) Wood
Cost: $6 to $9 per sq. ft, installed

Wood siding actually ranks quite highly for low environmental impact. It is sustainable, lasting for over 100 years if properly maintained. It is recyclable, and is a renewable resource.
Wood siding is made from a number of types of trees, including cypress, cedar, redwood, Douglas fir, pine, and cedar. NIST ranks cedar siding as one of the highest in eco-friendly siding options, beating out vinyl, brick, stucco, and aluminum.
Cedar siding is also less expensive to transport than other forms of siding because it is relatively lightweight. It is moisture resistant and repels insects, as well. It can be painted and stained, or you can seal it to retain the natural look.
Each area of the U.S. provides different types of wood. Red cedar is found in the Pacific Northwest, while white cedar is found in the eastern U.S. Yellow cedar is more native to the Southwest. To reduce your environmental footprint, select locally sourced wood for your siding.
Also, make sure your wood siding is certified as responsibly harvested. The Forest Stewardship Council, or FSC, and the Sustainable Forestry Initiative, or SFI, both oversee harvesting operations. They offer their own certifications to indicate that the management and harvesting of wood are environmentally friendly.
Wood is also a natural insulator. Wood siding has an R-value of 1, which is more than vinyl or metal siding.
Salvaged or Reclaimed Wood
Using reclaimed wood will make a big difference in your ecological impact. It requires diligence from you, and you will need to find a siding contractor that works with reclaimed wood. The ability to use salvaged wood makes a big environmental difference. This company uses reclaimed wood to great effect.
Bark Siding and Burnt Wood Siding
Bark siding is virtually maintenance free which makes it a good choice for sustainability. It is popular these days to use bark siding from poplar trees. This company has made burnt wood siding and bark siding an art form.
Burnt Wood Siding (Charred Siding)
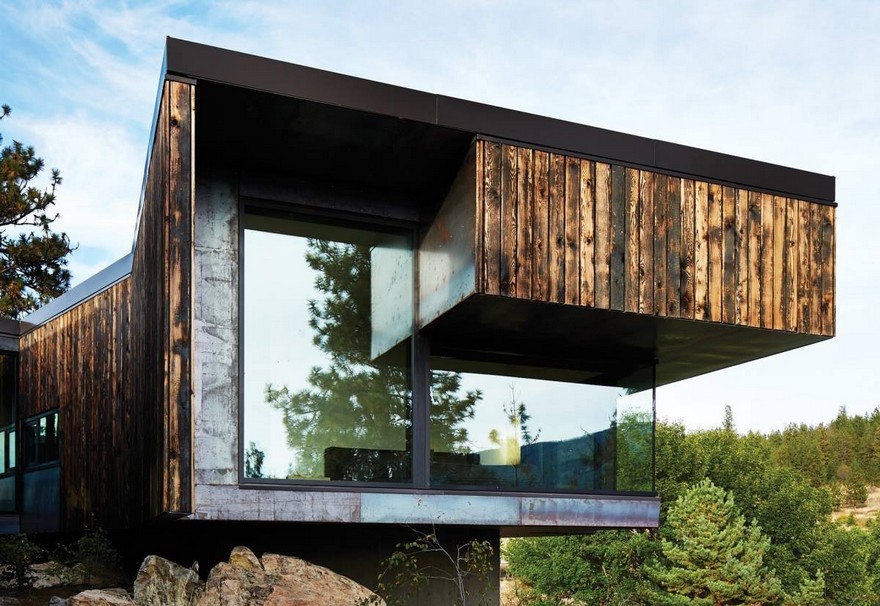

Burnt wood siding is a traditional Japanese siding treatment. Called “Shou Sugi Ban”, the wood is charred with fire, then finished out with Tung oil. Interestingly enough, this process actually makes the wood fire resistant and bug-proof. Burnt wood siding will last over 100 years without any kind of maintenance.
Engineered Wood
Engineered wood uses recycled products to make wood siding. A family company called Collins, and another company called Ecoclad make engineered wood siding that is certified as a green product By FSC. Ecoclad makes their siding from recycled bamboo fibers and paper.
2) Metal

Metal siding starts out on the plus side, because it is often made from recycled materials. Steel and aluminum are some of the most recycled metals in the U.S. In fact, the Steel Recycling Institute says that steel is the number 1 most recycled metal in the country.
Metal siding is also low maintenance, requiring little to no maintenance beyond the initial installation. However metal siding is heavy, and prone to being dented.
Steel is considered a greener alternative to aluminum because more of it is recyclable. One steel siding manufacturer, Rollex, produces a product that is 100% recyclable.
According to Revere Building Products, an average 2,000 sq. ft. home will use up to one acre of trees, if you select wood siding. However, the company can use 6 old cars to make the same amount of siding.
We compare vinyl and aluminum siding in this detailed break down.
3) Stucco
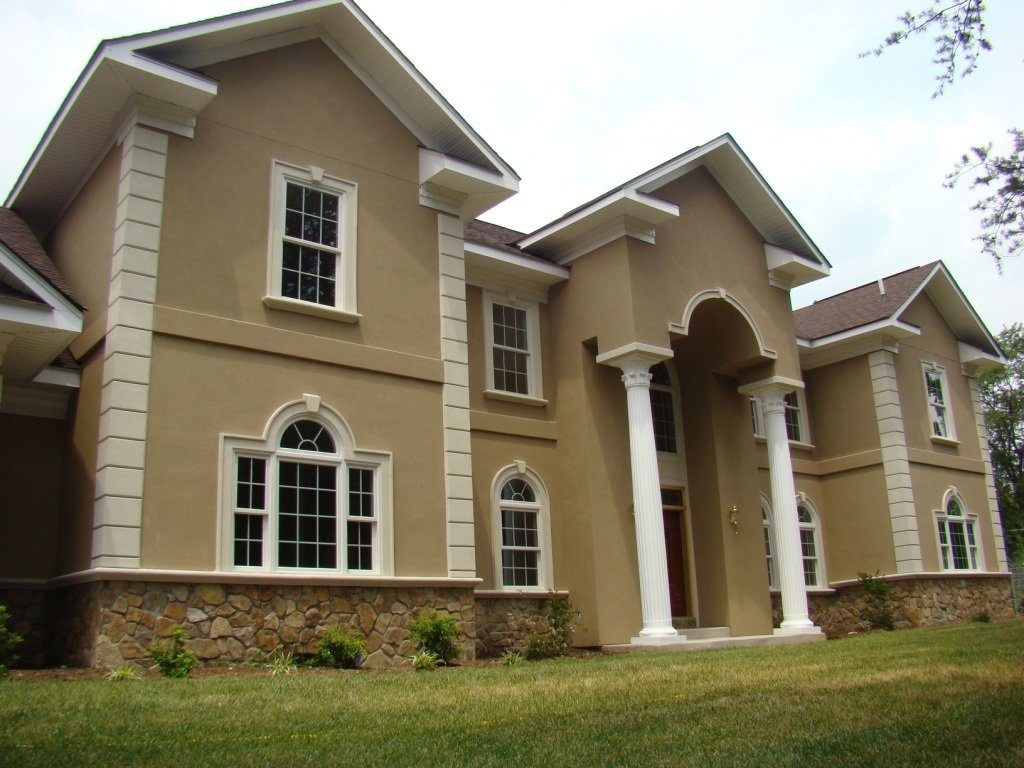

Cost: $6 to $9 per sq. ft. installed
Stucco siding is usually made from sand, water, lime, and Portland cement. People who live in arid climates prefer stucco because of its durability in dry conditions. All of the ingredients of stucco are natural, and it is usually made with no synthetics.
The use of lime plaster produces an even greener product. By leaving out the cement, greenhouse gasses are reduced, and the lime plaster is just as durable.
EcoStucco is one company that installs stucco siding. They provide well over 200 colors, and you can choose from four different textures.
When used as mortar, stucco can be removed from the brick. This makes it more likely that brick will be recycled, since cement mortar is much harder to remove.
EIFS
EIFS, or Exterior Insulation Finish Systems, is not used very commonly in residential structures, but is very common in commercial structures. Installed much the same way as stucco, there is less cement involved.
EIFS is an insulation board that has been coated with a waterproof acrylic sealant. This product is very lightweight and quite durable. One of the biggest selling points of this product is that is is one of the highest efficiency ratings of all the siding options. While its effect on temperature is minimal, it does reduce airflow and moisture.
4) Adobe and Earth Products
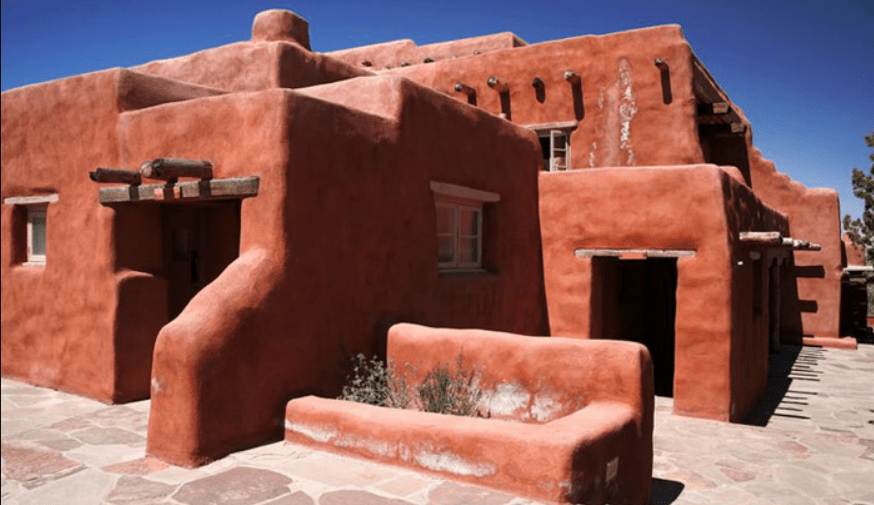

Adobe clay and brick are closely related to stucco. Adobe bricks are made in the same way the Israelites made bricks, with mud, water, and straw. They dry in the sun.
This is probably the most eco-friendly siding available. It is renewable, sustainable, and there is absolutely nothing to recycle when the siding is removed.
Adobe is considered to be the true epitome of sustainable construction, but it is usually installed as the house is erected. It is uncommon to see it in the suburbs. Locale is the main determinant as to whether or not you can request this type of siding. Most adobe houses are found in the Southwest, particularly New Mexico. If you live elsewhere and want an adobe house, you will have to pay to have the adobe bricks transported to your locale, which increases the environmental impact of the product.
Clay Mine Adobe makes adobe brick, along with the clay plaster used to finish the sides. Soledad Canyon also uses what they call a “rammed earth” process to produce adobe brick. You can also order synthetic adobe brick.
5) Fiber Cement
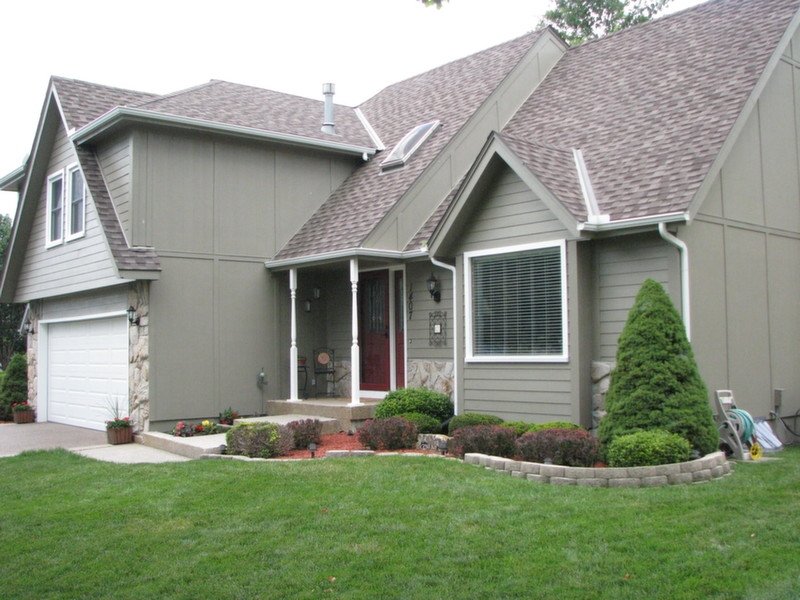

Cost: $5 to $9 per sq. ft. installed
Fiber cement siding is also a very green siding to use on your home. Once again, this product is made of natural materials, including sand, cement, and wood pulp. Hardie board is the most commonly used fiber cement siding in the U.S., but there are other manufacturers that are beginning to make a name for themselves.
Fiber cement emits less off-gasses during manufacturing than other forms of siding. When exposed to flame, it does not emit health-threatening fumes, as opposed to vinyl siding. This is a low-maintenance material that will last for upwards of 50 years with little maintenance. It is often used in place of wood siding, because it can mimic the look of wood.
Hardie board is manufactured under extreme heat, which is not good for its carbon footprint. Newer versions of Hardie planks use recycled materials and are more lightweight than previous models.
Another knock on the eco-friendly side of fiber cement planks is that they must be cut with saws. This releases silica dust, which is dangerous to breathe. In fact, the CDC is doing studies on whether this can be a problem on job sites. It is always recommended that, while in the process of cutting fiber cement siding, the worker uses a dust mask.
Fiber cement board siding has very little R-value. However, it also requires little maintenance because of its durability and resistance to warping and cracking. If you elect to install this product yourself, follow safety procedures to avoid inhaling the silica particles.
6) Brick

One popular, durable siding product is brick. This is an extremely low-maintenance siding, which makes it popular for both residential and commercial use. There is no need to caulk or paint brick, and it can be expected to last upwards of 200 years. The ingredients are natural, including clay, water, and shale.
However, it does take immense heat to manufacture brick. The clay bricks are baked in kilns for days at over 2000 degrees. The more ecological option is to use salvaged brick.
There are several manufacturers that produce more eco-friendly brick. Calstar reduces their CO2 emissions by using fly ash in their brick. This means they do not have to bake the brick as such extreme temperatures for as long. Each batch uses 500 million less BTU for baking and releases 80,000 pounds less CO2.
Green Leaf Brick produces brick made completely from recycled materials. These are also fired masonry.
Brick is very heavy. If you order brick from a remote locale, it will increase the environmental impact of the product because of the fuel needed for transport. It is usually better to use local sources for brick.
Brick veneer is another good option for siding. Companies such as TruBrix make brick veneer that uses the same materials and manufacturing process, but with greater volume because of the number of veneer pieces produced. These thin bricks are installed on metal railing and set with mortar, just as regular brick.
Your area may offer stabilized adobe brick. This is compacted earth that has had lime added. These adobe bricks are sun-dried, which eliminates the high-energy use of kilns.
7) Stone
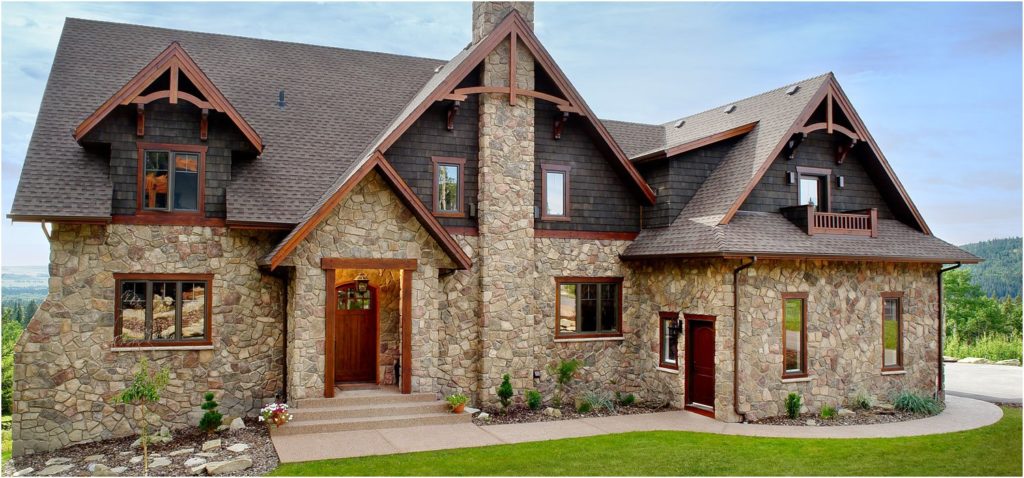

Stone siding lasts forever and is undoubtedly beautiful. It is a natural product, and requires no chemical treatment. Locally sourced stone will have to be mined, and it is heavy to transport, but once it is installed, it is there from now on.
Some stone-mining operations work to reduce their environmental footprint. Stone Wholesale Corp. works hard to leave their stone quarries in better shape than when they first started operations. They also use only energy efficient mining equipment.
While stone is very heavy to cut and transport, it requires practically no manufacturing. It is energy efficient, too, with an R-value that varies according to the thickness of the stone. Stone siding is recyclable if you take it down properly.
Stone veneer also gets high marks as environmentally friendly. Companies like Glacier Stone Supply provide stone veneer that is much thinner than the whole stone. It is natural, real stone, and greener in some ways because it doesn’t take as much energy to transport.
Faux stone siding is manufactured to look like real stone without the lengthy process of mining and cutting real stone. Genstone makes faux stone siding.
8) Vinyl

The most popular siding product is vinyl. It is used all across the country, but is it eco-friendly? This is often cause for great debate, much like the “paper shopping bag vs. plastic shopping bag” scenario. Vinyl siding is made of PVC, or Polyvinyl Chloride. This is, most definitely, not good for humans or the environment.
However, once the vinyl siding is manufactured, it is one of the most environmentally friendly products available. There is practically no manufacturing waste when producing vinyl siding, which is something other products can claim. It is also lightweight, so transport is more energy-efficient. This also makes it easier to install, especially as opposed to Hardie board, brick, or stone. It will need to be caulked and/or painted during its lifetime, but so do most other forms of siding.
When insulation is added to vinyl siding, it gets even better. This layer of thick foam is placed on the exterior wall, boosting the R-value of the finished product. The Vinyl Siding Institute works hard to redeem the reputation of its product, with plenty of examples of how vinyl siding is a green product. The sustainability of this product, combined with the ease of installation and low cost make it the most popular siding product in the country.
Insulated Vinyl Siding

Cost $3 to $8 per sq. ft installed
The cost of insulated vinyl siding is between 15% and 30% more than that of un-insulated siding. In some cases, the foam is attached to the wall of the house, and the vinyl planks are attached to the wall on top of the insulation. Most commonly, though, insulated vinyl siding is made by adding EPS foam to the underside of the planks. This makes the planks stiffer, which actually makes them easier to install.
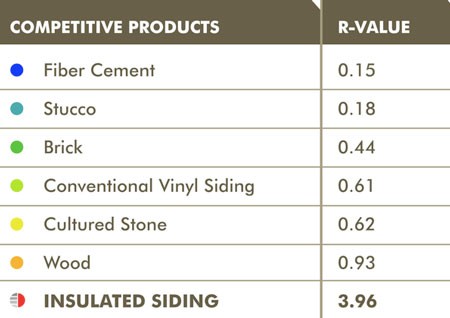
Vinyl and insulated vinyl are quite sustainable. They require little to no maintenance and can last upwards of 50 years. While it does not break down in landfills, it is recyclable. Insulation adds an R-value of 3 to your walls.
[Poll] What Siding Do You Prefer?
Other Ways to Improve Energy Performance
When you replace your siding, you have a golden opportunity to improve it. This is your chance to make your home more energy efficient and healthier. This can be accomplished with a house wrap. The wrap keeps water from seeping in, and performs as an air barrier. This also reduces the likelihood of mold and mildew developing in your walls.
Rigid-foam insulation is another factor that can improve the energy efficiency of your home. A typical home with fiberglass insulation has an R-12 rating. By adding rigid foam to the outside, you can increase that to as much as R-20. This can reduce your utility bills by 5% or more.
Adding a wrap and rigid foam insulation will cost about $1,800, but it increases your house’s energy efficiency, making it more eco-friendly.
House Wrap
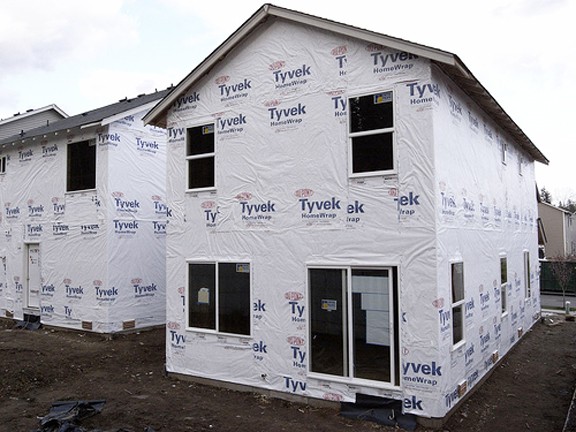

The cost of a house wrap ranges from 25 to 50 cents per sq. ft. installed. This is a very thin but tough fabric that is purposely designed to block water and air from passing through. This fabric is literally wrapped around your house over the sheathing and attached so that any fasteners are waterproofed. Rigid foam board and/or siding is then installed on top of the moisture barrier.
This increases the sustainability of your home, because this is an extremely durable product. It is also recyclable.
House wrap, when combined with properly installed siding in which the areas around the windows and doors are sealed, is very energy efficient. It can reduce your energy bills, in some cases by 5% a year. Some wraps are heat-reflective. DuPont’s Tyvek and Environmentally Safe Products’ Low-E Housewrap can increase your R-value by 2.
Rigid-Foam Sheathing
Adding rigid foam sheathing to your home’s exterior will cost between 20 cents and $1 per sq. ft. The thickness and R-value of the foam affect the price.
This is a light-weight product and can be applied to the outside sheathing of the house. It is recommended that a house wrap is used under this product to protect it and the house from moisture and air. It can be applied over existing siding and will provide a smooth surface for new siding. It is often used over asbestos siding in lieu of abatement proceedings.
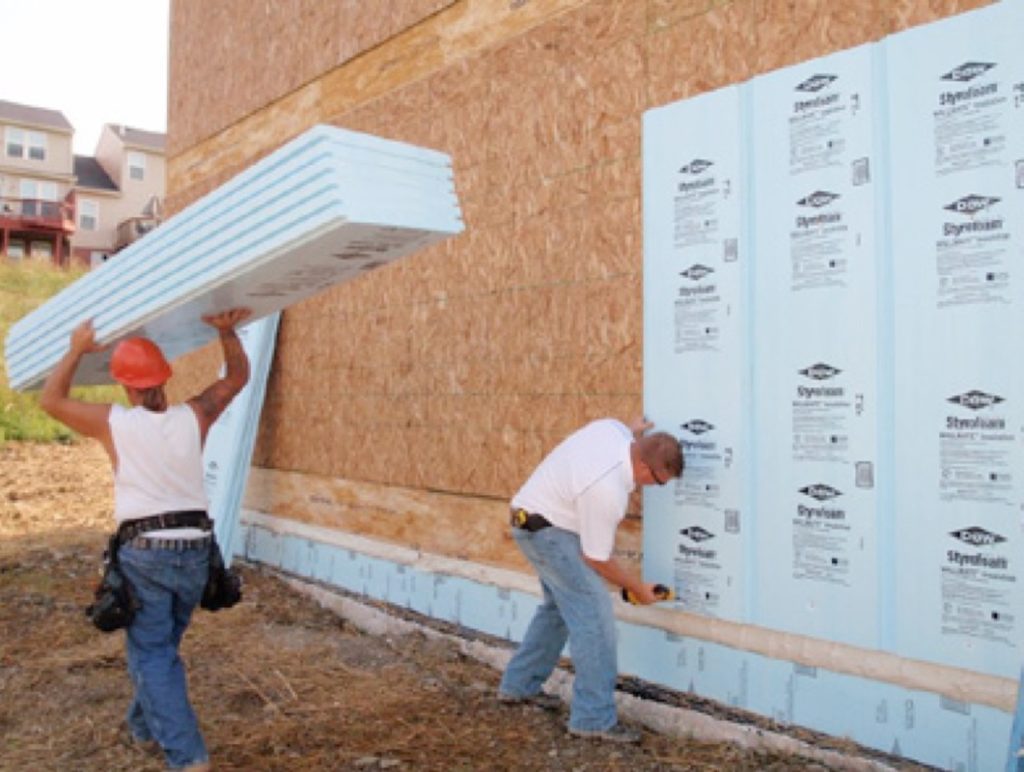

Rigid-foam sheathing is made from extruded polystyrene, or XPS. This produces CFCs, which have been determined to damage the ozone. Some manufacturers are experimenting with Expanded polystyrene (EPS) rather than XPS. This does not produce CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons). While EPS can be recycled, neither this nor XPS will break down in landfills.
Each inch of thickness in rigid-foam sheathing will provide R-3 to R-7 in insulation.
What to Read Next
Over to You
Where do you stand on the issue of eco-friendly construction? Let us know by leaving a comment below!
